Quick fix for DSMLs
Authors: Ábel Hegedüs, Ákos Horváth, István Ráth, Moisés Castelo Branco and Dániel Varró
This page contains additional information for our paper Quick fix for DSMLs. We include here a simplified BPMN metamodel, the list of inconsistency rules and operations for the BPMN case study used in the paper.
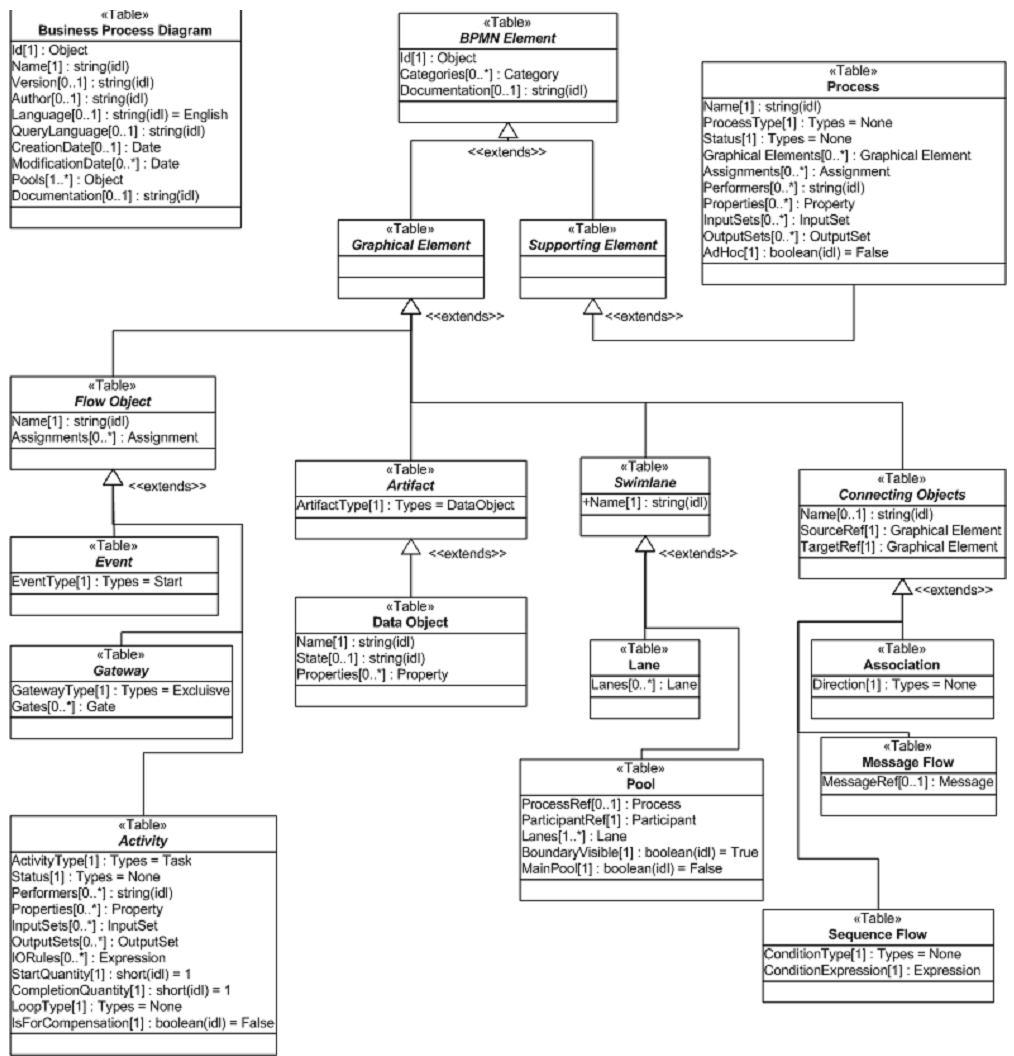
BPMN metamodel (simplified)
List of inconsistency rules for BPMN
| The gateway should have a default gate to ensure that at least one gate will be valid at runtime. |
| There is no need for a default flow since there are no controlled flows out of the activity. |
| This flow is marked as default while there are no other edges going out of the activity. |
| The default path will never be executed since there are uncontrolled flows going out of the activity. |
| This sequence edge is marked as conditional while there are no other edges going out of the activity. |
| Conditional flows should not be preceded by gateways. |
| End event should not be the start point of a sequence edge. |
| Start event should not be the end point of a sequence edge. |
| A message cannot be sent between elements of the same pool. |
| An intermediate event must not send a message. |
| A start event must not send a message. |
| An end event must not receive a message |
List of operations
| Create/remove sequence edge |
| Change source/target of sequence edge |
| Change default attribute of sequence edge |
| Change conditional attribute of sequence edge |
| Create/remove message edge |
| Change source/target of message edge |
| Change default attribute of message edge |
| Change type of Event (Start, Intermediate, End) |
| Change type of Gateway |
| Change subtype of Event (Link, Message, etc.) |
| Create/remove Activity (Task, Gateway) |
Acknowledgment
This work was partially supported by the SecureChange (ICT-FET-231101) and CertiMoT (ERC\_HU\_09) projects and the Janos Bolyai Scholarship.
We would like to thank the Bank of the Northeast of Brazil (Banco do Nordeste – BNB) for providing the case study.